Tides
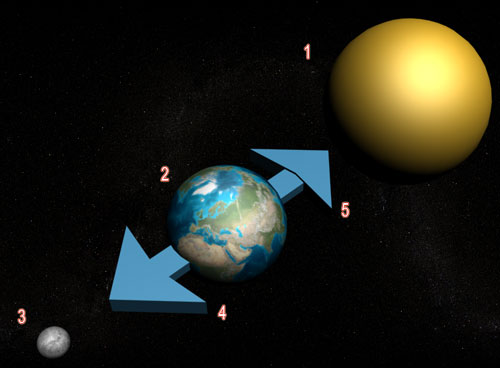
The highest tides, called spring tides, are formed when the earth, sun and moon are lined up in a row. This happens every two weeks during a new moon or full moon.
Smaller tides, called neap tides, are formed when the earth, sun and moon form a right angle. This causes the sun and moon to pull the water in two different directions. Neap tides happen during a quarter or three-quarter moon.
The width of the shoreline strip that is affected by waves depends on the tidal range. A large tidal range means that a wide strip of land might be subjected to the force of the waves. If the tidal range is very small, all of the wave's energy will be concentrated in the same place.
The rise and fall of tides causes water  to move in and out of estuaries, bays and harbours. This movement is called a tidal current. When the tide is rising, water flows from the ocean into the bay creating a flood current. When the tide falls, water flows from the bay back into the ocean creating an ebb current.
to move in and out of estuaries, bays and harbours. This movement is called a tidal current. When the tide is rising, water flows from the ocean into the bay creating a flood current. When the tide falls, water flows from the bay back into the ocean creating an ebb current.
« Back